Mobile payment, whereby all the payment transactions are carried out from a mobile phone, is more precisely the payment of certain purchases of goods and services or money transfer from our mobile devices. These payments are usually charged to: a bank card, a telecom operator invoice or an electronic wallet.
Until recently, our purchases were made by a credit card, check or cash; now, thanks to the internet, new payment systems have emerged, such as payment by mobile terminals with NFC (Near Field Communication ). With mobile payment, the boundaries between traditional and electronic commerce are disappearing. With connected mobile terminals you can choose the product or service on the Internet and these devices can pay for what you choose. In the first quarter of 2015, mobile payment represented almost 29% of total online payments, according to Adyen, a specialist in international payment solutions.
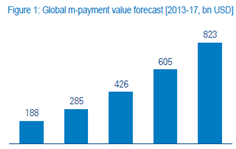
M-payment including NFC represented a total of 285 billion USD in 2014 and Arthur D. Little firm expects that these numbers will keep growing at a rapid pace and can exceed $800 billion by 2017 .
With this payment method, we are witnessing the emergence of new players that are gaining an increasing market share every day. These new players of mobile payment are the classic operators of bank cards like Visa, dynamic payment actors in e-commerce such as Amazon, and new ones that are more qualified in mobile payment as Google Wallet, telecom operators and operating system suppliers like Android system.
If banks don’t evolve following this trend, then these new aforementioned actors can surpass them. After missing the turn of Internet payment, banks also may not succeed in mobile payments. The emergence of new players could seriously disrupt the business model of banks. As new players settle, banks will gradually lose customer knowledge. This knowledge is essential because it allows the development of service offerings and helps build partnerships for the bank. The Davos Economic Forum 2016 edition provides a total digitalization of banks in 10 years, as part of the discussion on the fourth industrial revolution, which could lead to the end of cash and bank branches in probably ten years. The contactless mobile payment system Apple Pay is successful with large companies and large food chains. Apple has already signed more than 500 agreements with banks and it is going to equip more than 220,000 points of sale of an American fast food chain.
Global m-payment by 2017 in billions USD. Source : Arthur D. Little
In Morocco, the debate around the mobile payment has begun. A new law was adopted in Morocco to prepare it for this technological breakthrough. It is the Law No. 103.12 on similar credit institutions and organizations, adopted in November 2014 called « banking law ». This new banking law enlarge the scope of means of payment by acknowledging for the first time electronic money. Electronic money is defined as any monetary value representing a claim on the issuer being stored on an electronic device, issued in consideration for the receipt of funds of an amount whose value is not less than the monetary value issued and accepted as means of payment by third parties other than the issuer of electronic money.
In Morocco mobile payment could start from the payment for the public transport ticket that already exists in the West. Morocco also seems to be moving towards this solution which is the use of mobile phones for ticket payment and many organizations are conducting experiments in this direction like the operator of tramway.
There are three types of mobile payment: contactless payment, remote payment as mobile payment on e-commerce sites and mobile-to-mobile money transfers.
1-Contactless Payments: Contactless payment is based in most cases on a technology called Near Field Communication (NFC). This NFC technology based on the use of a wireless communication protocol or « contactless » short range of less than 4 cm, enabling the exchange of information between two devices such as a mobile terminal and a electronic payment (TPE). To make the payment, the user must pass his mobile phone on the TPE and possibly validate its settlement by a code, especially when it is a big amount of money. In order to execute the operation it is necessary that the mobile device is equipped with a NFC chip and that the merchant has previously installed a contactless payment application on his TPE. In fact, Google is leading the mobile contactless payment solutions with its Google Wallet. Bluetooth may also be used for payment through a terminal. This is a wireless connection that has both advantages and disadvantages compared to NFC. Bluetooth can reach 50 m, NCF 4cms. For example Bluetooth mobile payment application from Apple allows the implementation of several new developments in the field as the fact to guide customers in the commercial center after having been detected and identified. In practice, we find that most Bluetooth devices are also equipped with NFC. Some precautionary measures should be taken with NFC. So for example in France, for payments of up to 20 Euros, the merchant enters the amount on the terminal and the consumer put his mobile less than 4 cm from the card reader and the transaction is done. The consumer does not even have to unlock or to manipulate the interface of the phone. For payments above 20 Euros, after introducing the mobile device in front of the terminal, the consumer must enter their PIN on their mobile phone and then reintroduce it to the card reader to complete the payment.
2-Remote Payment: This is the mode of payment which is currently the most used in the world including Morocco. Online consumers first choose what to buy and pay directly on the Internet through a dedicated application for online payment. Apple Store is an example of remote payment for application purchases. Moroccan subscribers with a connected mobile phone may purchase or pay their debts via their mobile with scurried mobile version of online payment made by Morocco Télécommerce that has been adapted to this service. SMS can also be used in some cases as mobile remote payment method. In exchange for a surcharged SMS, the user receives on his phone an application or a purchased service. So he pays via his mobile bill. The operator is then responsible for paying the original supplier. This service is working well in Morocco by providing various services through special numbers within the agreements between mobile operators and service providers . In France, exactly in Montpellier, it is already possible to pay the parking charges by a remote mobile solution developped by the PayPoint group.
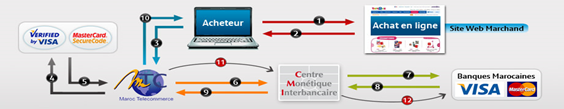
Internet payment architecture in Morroco
3- Mobile to Mobile Money Transfer is developed especially in some countries in Africa. Kenya is a good example where the service has been very successful. Beyond the classical actors of domestic and international money transfer as Western Union, many phone companies offer e-money accounts associated with the mobile number, giving access to a range of services including money transfer, paying bills and buying airtime. In Morocco, mobile to mobile money transfer in the same telecom operator network was launched in 2010 by some operators, under Law No. 34-03 on credit institutions and the Law 24 -96 on telecoms. Despite a massive advertising campaign, the new service was not successful , considering the fact of the higher banking rate in Morocco besides the large presence of post offices and agencies like Western Union. The national Post Office, which also acts as a bank, had at the same time some 1 600 branches, 70% in rural areas and 30% in urban areas.
-
A futuristic payment system called «hands free » Google being tested in San Francisco USA. Google has implemented a payment system called Hands Free requiring only the use of hands to pay in stores. So all you need is a smartphone on itself and say » I want to pay with Google , » without taking it out of his pocket or her purse. This new payment system that uses Bluetooth LTE or Wi- Fi to detect that the client is well in the shop where he wants to make the payment. For more information, see the following link: http://www.presse-citron.net/oubliez-le-paiement-nfc-google-teste-une-solution-mains-libres/.